Search
Geographic Origins: Petersburg
18 Results
Novikov's New Russian Classicism: Pop Culture, Fashion, and Totalitarianism
Timur Novikov’s essay and manifesto “The New Russian Classicism.”
The First (Home-Made) Post-Soviet Independent TV
The Saint Petersburg “New Artists” stage a meeting of the committee “anti-state of emergency” on their “Pirate Television,” declaring their support of Yeltsin against the group of communist hardliners who led the coup d’etat against Gorbachev on August 19, 1991.
The World Made of Plastic Has Won
Egor Letov performs his song “Moia oborona” (My defense), during his “concert in the hero city Leningrad,” part of Grazhdanskaia oborona’s 1994 tour Russkii proryv (Russian breakthrough).
Romantics and Fascists
Kuryokhin explains his definition of fascism and his distinction between mainstream postmodernism and a postmodernism of protest.
"What is Concealed Will Be Revealed." Kuryokhin's and Dugin's Post-Ironic Political Campaign in Saint Petersburg
An episode from Dugin's political campaign in Saint Petersburg, in which Sergey Kuryokhin and Aleksandr Dugin make fun of liberal democracy (and Yeltsin’s referendum) on Russian TV.
"Only the Wildest and Craziest": Kurekhin's Neo-Avant-Garde on Radio-1, Petrograd
An episode of Kuryokhin’s radio program “Vasha liubimaia sobaka” (aka “Nasha malenkaia rybka,” aka “Russkii liudoed”).
Lenin Was a Mushroom
An excerpt from the famous episode of the TV show Piatoe koleso in which the experimental musician and performer Sergey Kuryokhin argued and almost convinced Soviet audiences that "Lenin was a mushroom."
Gorodok [Little Town]: 1993-2012
title screen, "Little Town"/"Gorodok" by Iurii Stoyanov and Ilya Oleinikov, 1996
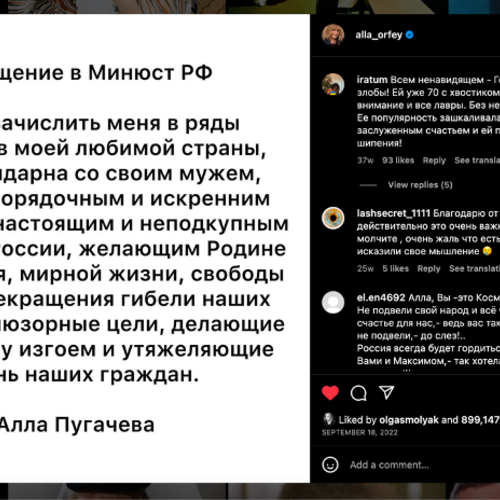
Alla Pugacheva — Post-Soviet Diva
The most famous woman in the Soviet Union transformed into a successful post-Soviet star.
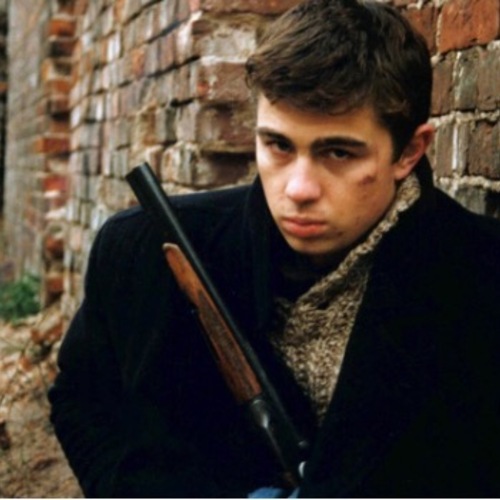
Brother. Motion Picture. Dir. Aleksei Balabanov (Excerpts)
Aleksei Balabanov's cult crime drama, which made its title character, the loveable killer Danila Bagrov into a youth idol and a national emblem of post-Soviet masculinity
Shevchuk (DDT) in Chechnya
Excerpt from Vremia DDT, a 2002 documentary centered on DDT, one of Russia’s most famous rock bands throughout the 1990s and later. A montage of amateur film made by the group leader and frontman, Yuri Shevchuk during his visit to Russian frontlines during the First Chechen War in 1995-1996, overlaid by the song, “Patsany [The guys],” inspired by what Shevchuk saw there.
Mat bez elektrichestva. (Profanity without electricity). A ska-punk-rock album by Leningrad. (Cover art and excerpts)
The second studio rock/ska album by the legendary St. Petersburg band Leningrad. With its heavy use of profanity, the album etablished Sergei Shnurov as the band's unequivocal frontman and placed Leningrad on the map as a new and influential direction in post-Soviet rock music.
TaMtAm Rock Club documentary by German television (1993)
The first and until 1994 the only Western-style rock club in Russia, which was founded in 1991 by cellist Vsevolod (Seva) Gakkel (Akvarium) after he visited the famous music club CBGB in New York. The club specialized in punk rock specifically, providing the budding underground punk scene in Russia a much-needed performance venue and cultural legitimacy. Some have accused Gakkel's establishment for breeding far-right nationalist sentiments among Russia's youth subcultures (or at least providing them with a physical organizational platform) in the early 1990s. The fact that a German television production company took interest in TaMtAm is also a testament to punk as a truly transnational movement after fall of the Berlin Wall.
Soviet Homosexuals: Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow
Essay by gay former Soviet inmate published in journal Gay, славяне!
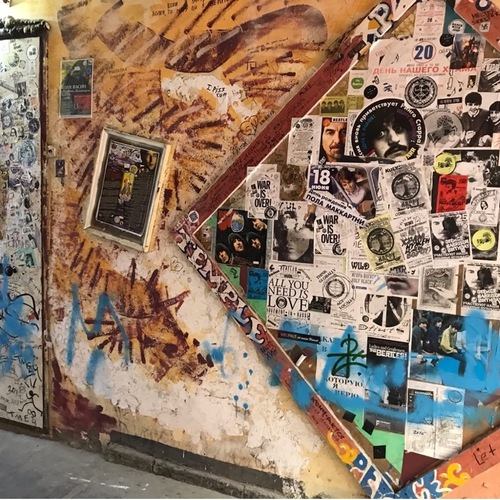
Kolia Vasin’s petition for the “John Lennon Church of Rock-n-Roll” (Khram Rok-n-rolla imeni Dzhona Lennona.) in St. Petersburg (April 1992).
An official petition for the establishment of the so-called "John Lennon Church of Rock-n-Roll" in St. Petersburg, conceived by the self-described "Beatlelologist" Kolia Vasin, a major personality in and driver behind the formation of Leningrad's rock music community.
Revisiting Tchaikovsky's Supposed Suicide: Rebuttal
Article disputing accounts of Tchaikovsky’s suicide in the face of having his homosexuality broadly divulged.
Alexei Uchitel's 1992 documentary film Posldenii Geroi.
Made with the collaboration of Tsoi's widow Marianna Tsoi, the film includes scenes from Viktor Tsoi's funeral and chronicles the mass mourning of the late musician, and the perestroika era by proxy.